Models of Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury (HIBD), or hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE), is a type of newborn brain damage caused by intrapartum hypoxic events, and a major cause of acute mortality and chronic neurological morbidity worldwide. Currently, HIE is commonly managed using hypothermia treatment and supportive care. However, these are not curative. They have shown improvement only in mild to moderate HIE.
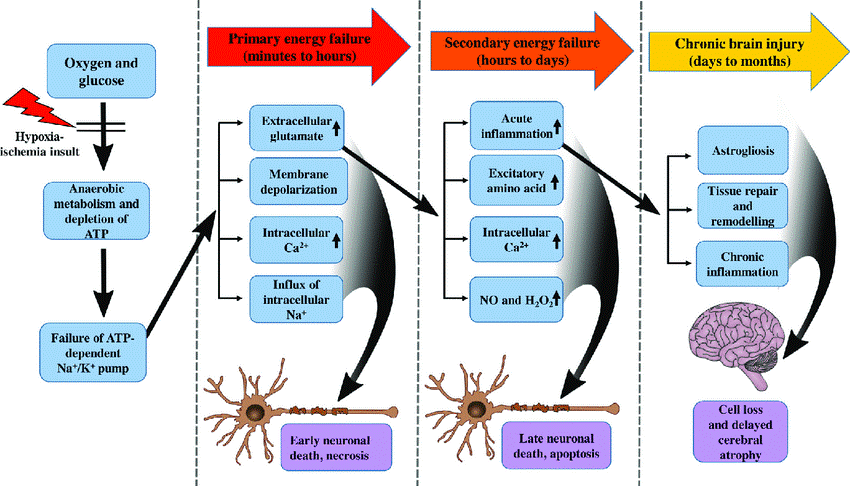
Figure 1. The pathogenesis of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (Li et al. 2017).
Our Models of Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy
Greentech provides the following validated in vivo models for assessment of HIE.
1. Modified Rice-Vannucci Model - Unilateral Carotid Artery Occlusion HIE Model, UCAO
Induction: after post-natal Day 7 rats are fully anesthetized, a small incision is made in the middle of the neck. Right common carotid artery (RCCA) is then occluded and transected, and the incision is closed with sutures, followed by 8% hypoxia at 37℃ for 2.5 hours.
Pathological Characteristics: severe cerebral tissue damage, partial necrosis of surviving neurons, karyolysis.
Advantages: a classical and well-accepted method for establishing HIE model, high success rate, easy operation.
2. Tracheal Occlusion HIE Model
Induction: after post-natal Day 7 rats are fully anesthetized, the trachea is occluded with vascular clamp for 10 min.
Pathological Characteristics: tracheal occlusion HIE model resembles clinical pathological features of brain injury, including tissue bleeding, necrosis, and neuronal apoptosis.
Advantages: flexible and controllable hypoxia period, easy operation, high similarity to clinical resemble.
Animal Species
SD rats
Clinical Assessment
(1) Neurological evaluation (using a five-point Zea-Longa score)
(2) Brain weight
(3) Histopathology: HE, TCC, TUNEL staining
(4) Behavioral tests: Morris water maze, Cylinder test, Rotarod test
Features
- Equipped with neurobehavioral evaluation, histopathology and other supporting facilities
- Extensive experience in building animal models of neurological disorders
- Experienced neurologic researchers and full-time veterinarians lead the team
References
1. Lee J A, Kim B I, Jo C H, et al. Mesenchymal stem-cell transplantation for hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rat model[J]. Pediatric research, 2010, 67(1): 42-46.
2. Li B, Concepcion K, Meng X, et al. Brain-immune interactions in perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury[J]. Progress in neurobiology, 2017, 159: 50-68.
3. Lee J A, Kim B I, Jo C H, et al. Mesenchymal stem-cell transplantation for hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rat model[J]. Pediatric research, 2010, 67(1): 42-46.
Inquiries
Request a quote now, or email us at BD@greentech-bio.com to inquire about our services or obtain a quote for your project.