Models of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic, progressive lung disease in which abnormal wound healing causes a scarring of the lungs and breathing becomes increasingly difficult. Unknown etiology makes drug development challenging. Greentech Bioscience offers IPF models for preclinical drug efficacy testing, including bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis model and silicon induced pulmonary fibrosis model.
Our Models of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
1. Bleomycin Induced Lung Fibrosis Model
Intratracheal instillation (IT) of bleomycin is a widely used experimental model for studying mechanisms related to IPF and to evaluate the effect of anti-fibrotic therapies. This model induces an early inflammatory phase and subsequent develops progressive fibrosis after 5-7 days. This fibrotic phase typically lasts two weeks. Bleomycin induced lung fibrosis is a relatively inexpensive model that mimics the histological manifestation of IPF in human patients.
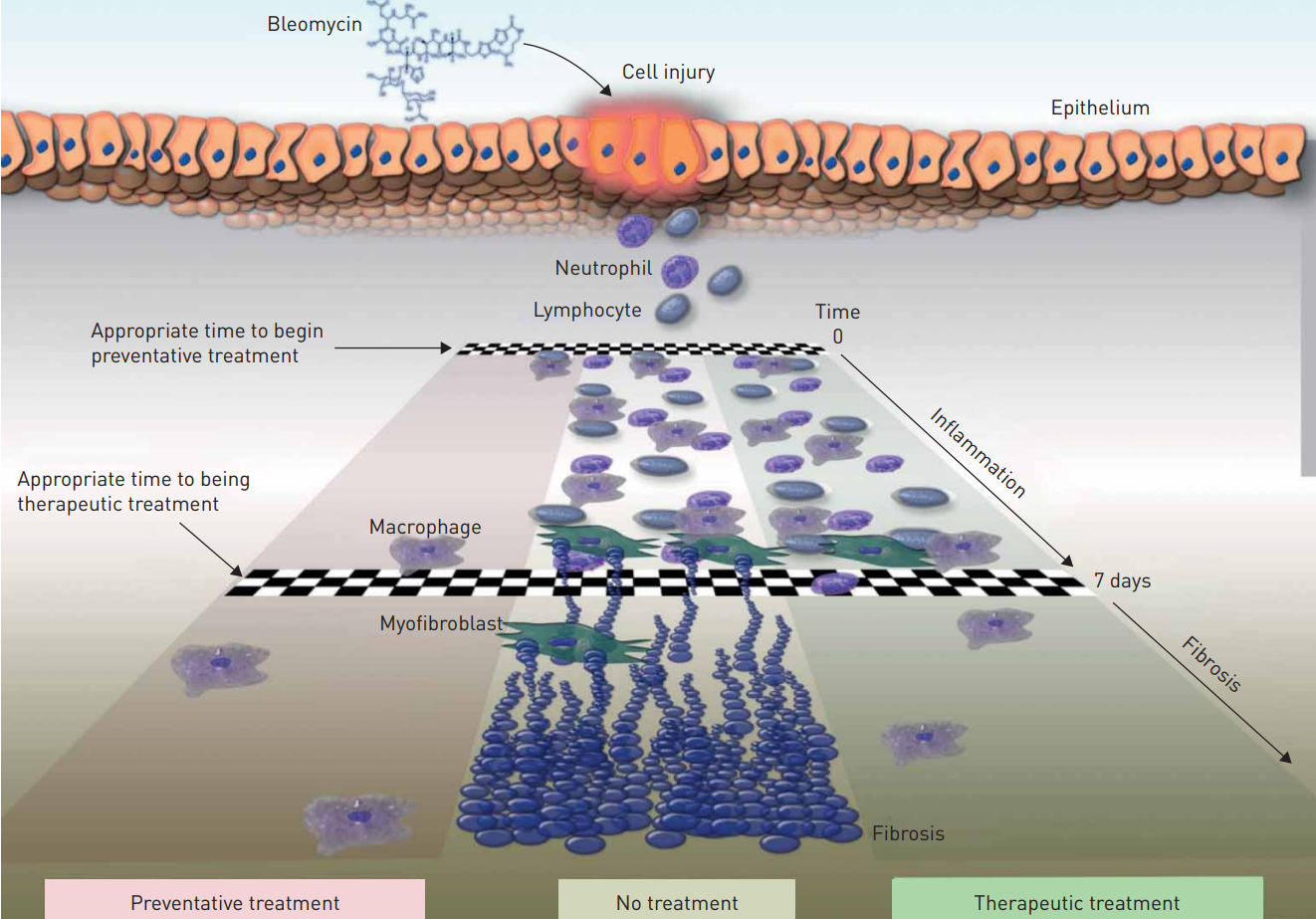
Figure 1. Illustration of the appropriate times to start intervention in the model of bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis (Kolb et al., 2020).
2. Silica Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Model
Although lung fibrosis induced by bleomycin is widely used, long-lasting disease activity in silica-induced lung fibrosis contributes to its appeal. Silica induced lung fibrosis is induced after silica inhalation in rodents. Since silica particles are not easily cleared in the lungs, they tend to keep stimulating the lungs, causing lung inflammation and fibrosis for as long as 24 weeks.
Animal Species
Rats, golden hamsters
Clinical Assessment
(1) Body weight
(2) Inflammatory cell count of the bronchoalveolar lavage fluids (BALFs)
(3) Measurement of hydroxyproline
(4) Histopathology: H&E, Masson, etc.
Case Study
1. Bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis model
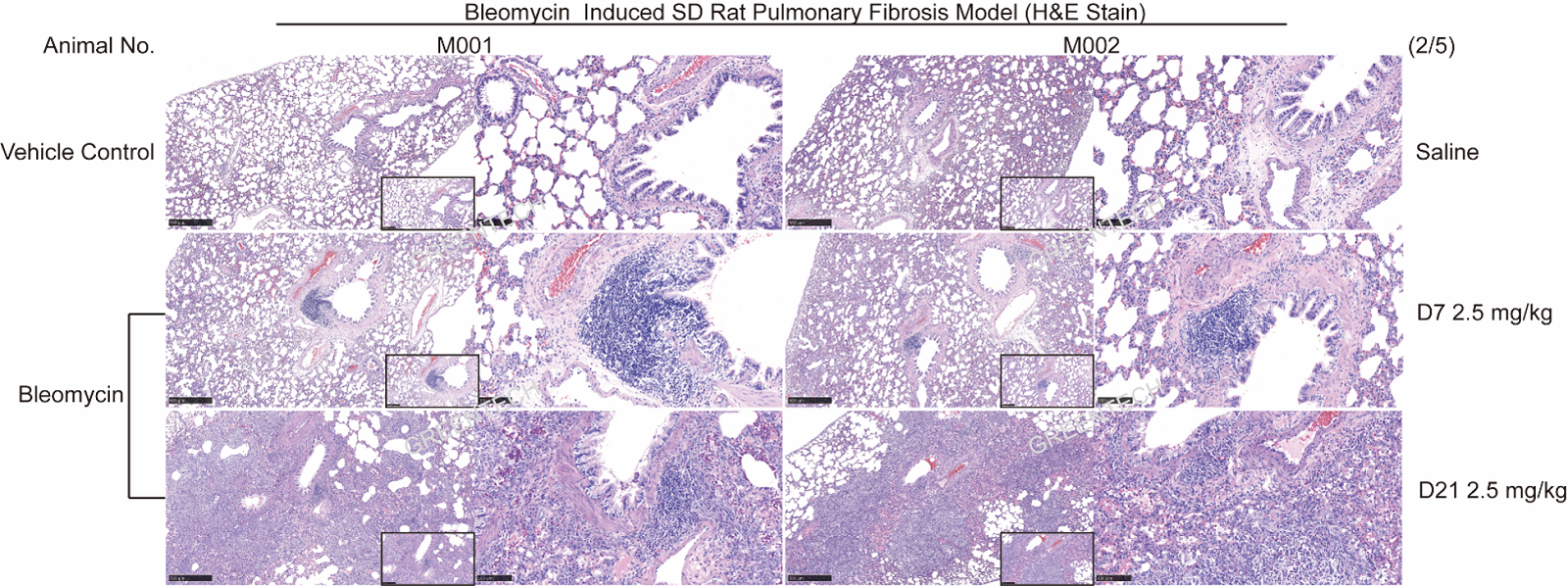
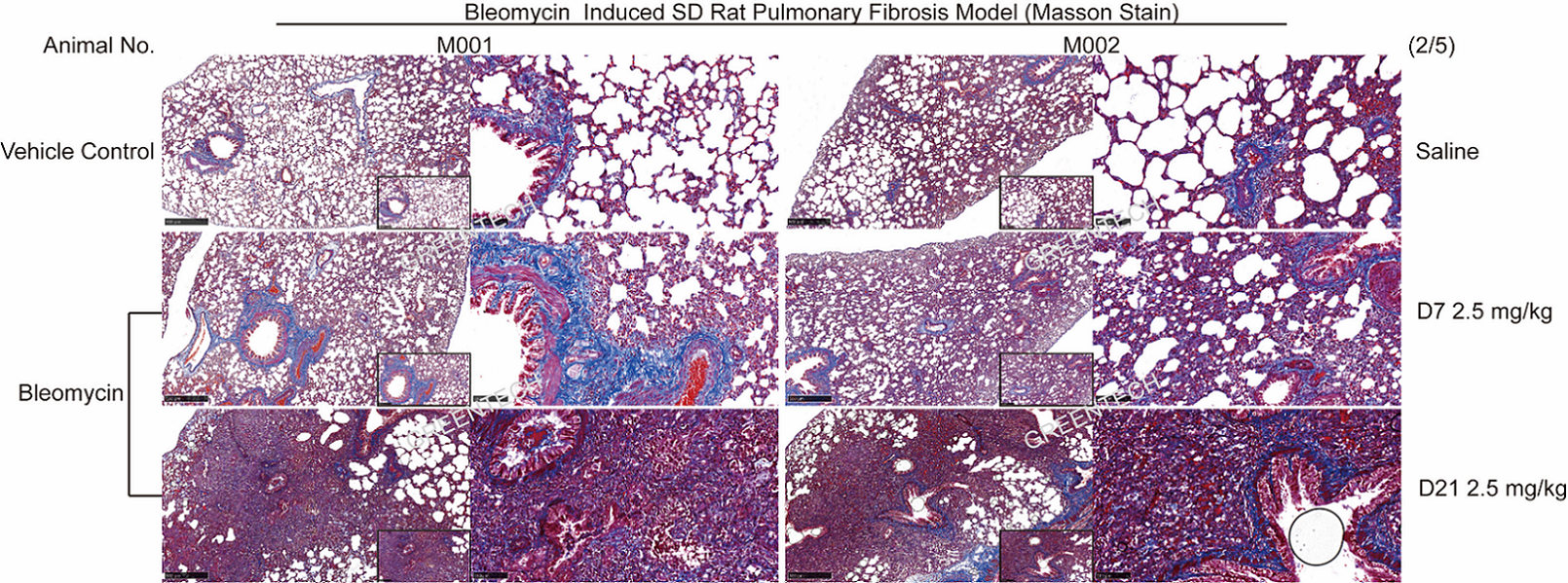
Figure1. Lung section staining of bleomycin induced pulmonary fibrosis model in rats.
2. Silica induced pulmonary fibrosis model
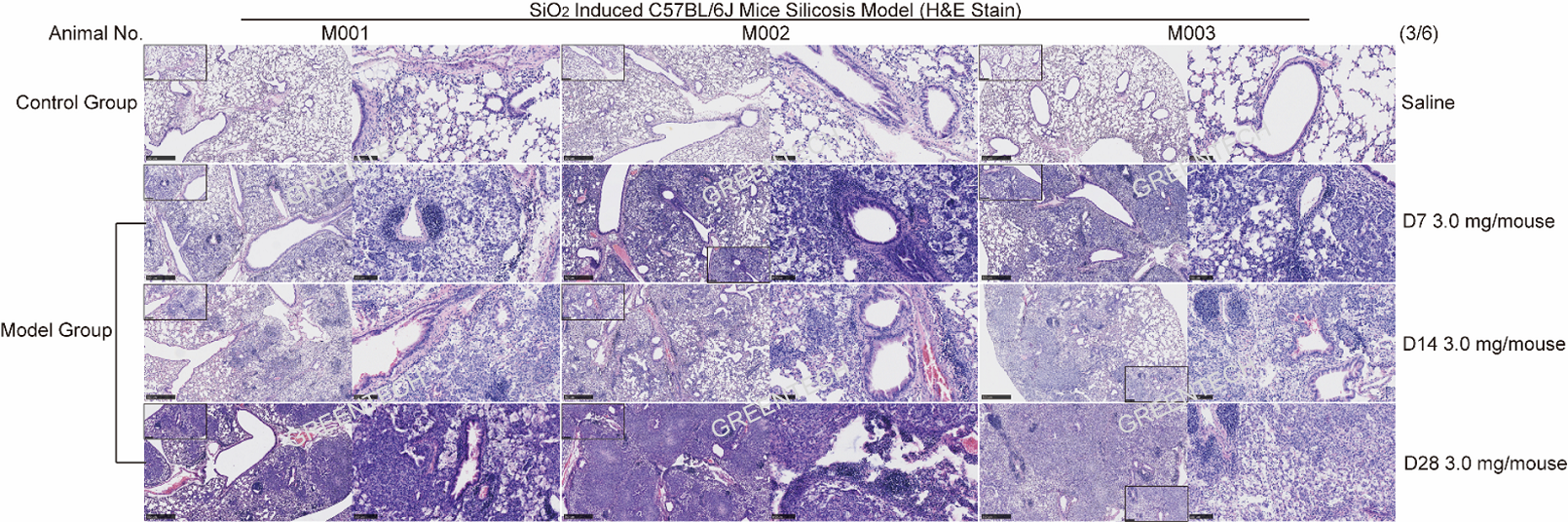
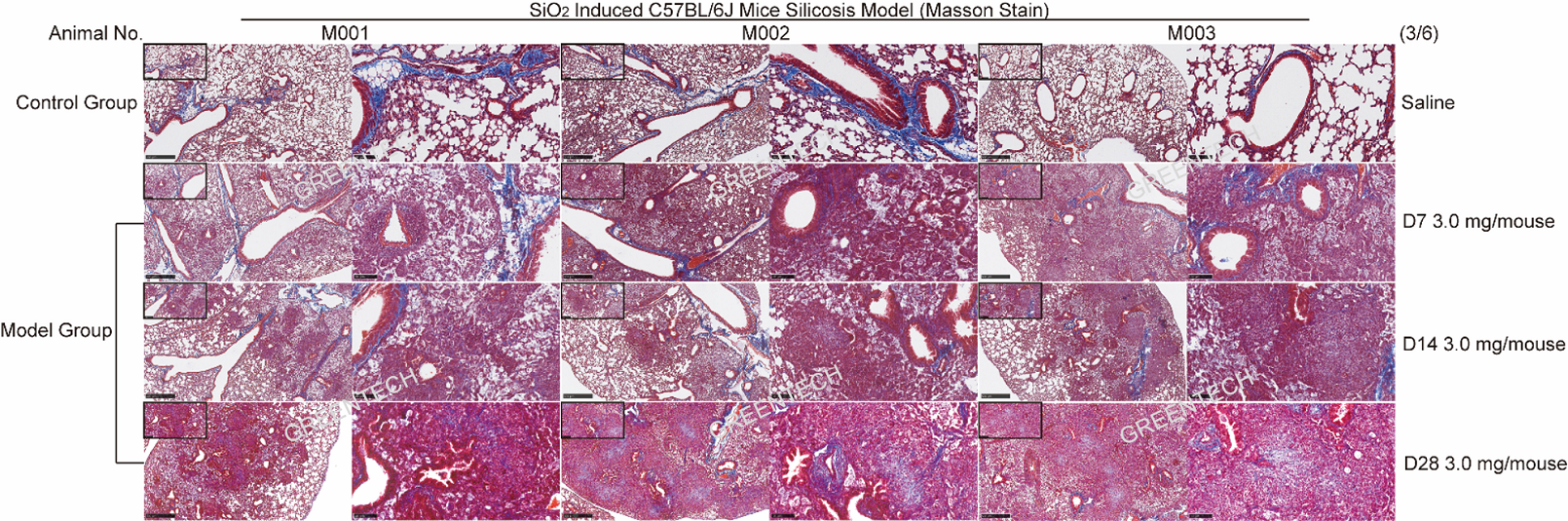
Figure 2. Lung section staining of silicon induced lung fibrosis model in mice.
References
1. N.R. Simler, et al. The rapamycin analogue SDZ RAD attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. European Respiratory Journal Jun 2002, 19 (6) 1124-1127.
2. Kolb P, et al.The importance of interventional timing in the bleomycin model of pulmonary fibrosis.[J].Eur Respir J,2020,6.
3. Sugimoto N, et al. IL-9 Blockade Suppresses Silica-induced Lung Inflammation and Fibrosis in Mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019 Feb;60(2):232-243. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0287OC.
Inquiries
Request a quote now, or email us at BD@greentech-bio.com to inquire about our services or obtain a quote for your project.