Models of Postoperative Pain
Management of acute pain related to post-operative pain (POP) continues to be a major healthcare challenge. Unrelieved POP causes severe discomfort, even leading to psychological and pathophysiological complications. Greentech Bioscience offers validated rat plantar surgical incision model and porcine skin incision model for in vivo drug efficacy testing. Greentech Bioscience is committed to offering preclinical pharmacological studies in compliance with GLP requirements.
Animal Models of Postoperative Pain
Animal models of postoperative pain (POP) are vital for mechanism studies and development of novel analgesics used to reduce or eliminate postoperative pain. Incisional pain in rats or pigs that cause violent, acute pain and chronic pain, can mimic invasive surgeries in humans.
1. Rat Plantar Incision Model
The rat model of incisional pain is a classical experimental model in the study of POP. Briefly, the rat plantar incision model consists of 1-cm longitudinal incision in the hindpaw and wound suture. Hindpaw incision in rats produces acute hyperalgesia and significant changes in mechanical withdraw threshold (MWT) and thermal withdrawal latency (TWL). However, the rodent model is limited for topical application due to the relatively small rat hindpaw.
2. Porcine Incisional Pain Model
The anatomy of porcine skin exhibits a high degree of homology to human skin. Hence, pig models have become a standard model of wound healing and inflammatory pain. The pig model of incisional pain model has been a popular model of postoperative pain. Nociceptive behavior using the Von Frey test and spontaneous pain-like behaviors can be evaluated or observed.
Clinical Assessment
(1) Clinical observations
(2) Behavioral test: mechanical hyperalgesia (Von Frey test) and hot plate test (only for rats)
Case Study
A porcine model of post-operative pain
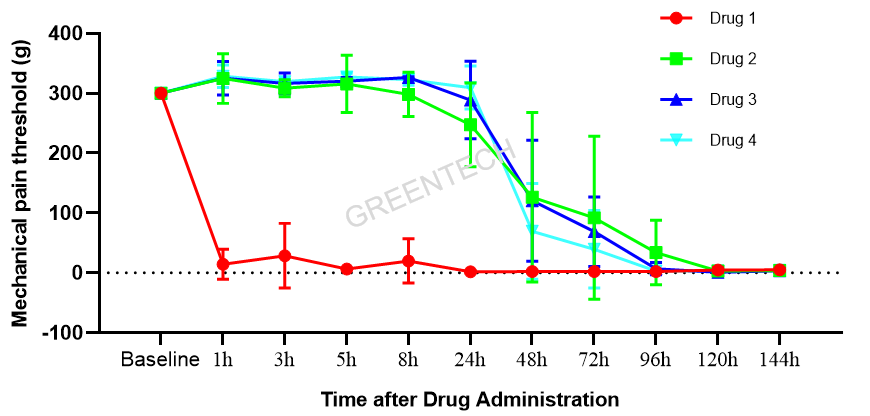
Figure 1. Mechanical pain thresholds in a pig incisional pain model.
Inquiries
Request a quote now, or email us at BD@greentech-bio.com to inquire about our services or obtain a quote for your project.
References
1. Castel D, et al. Characterization of a porcine model of post‐operative pain. European Journal of Pain, 2014, 18(4):496-505.
2. Xu Ding, Wei Yang, Xiao-Dan Liu. Spinal SHP2 Contributes to Exaggerated Incisional Pain in Adult Rats Subjected to Neonatal and Adult Incisions via PI3K. Neuroscience. 2018 Aug 10;385:102-120.