Models of Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
Parkinson’s disease is a chronic neurodegenerative disorder characterized by dopaminergic (DA) neuron death in the substantia nigra compacta (SNc) and the accumulation of aggregated α-synuclein (α-syn) into Lewy bodies (LBs). To date, there is no cure for PD, but there are medications to address some of the symptoms. Greentech offers validated animal models of Parkinson’s disease for studies of biological mechanisms and assessment of novel therapies.
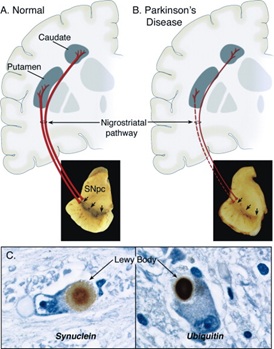
Figure 1. Neuropathology of Parkinson's Disease (Dauer & Przedborski 2003).
Our Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease
1. MPTP Induced Parkinson’s Disease Model
The 1-methyl 4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP), a dopaminergic pyridine neurotoxin, has been commonly used to mimic Parkinson's disease in mice. The MPTP induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease is a cost-saving and time-efficient solution for PD research. MPTP-induced parkinsonism in the monkey is considered as the gold standard PD model because it reproduces some of the critical pathophysiological and behavioral alterations in humans.
Induction: intramuscular injection, intravenous injection, intraperitoneal injection, cervical artery injection, or injection into the substantia nigra.
Animal Species: mice, non-human primates (NHPs)
Disease Characteristics: MPTP-induced PD model exhibits neuropathology similar to PD, including nigrostriatal dopaminergic cell death and loss of their neurotransmitter, dopamine (DA), in the striatum.
2. 6-OHDA Induced PD Model
6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) is a catecholamine neurotoxin, widely used for modeling degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in PD. Since 6-OHDA cannot cross the BBB, it is often administered locally into the striatum, SNpc, or medial forebrain bundle (MFB) to establish unilateral 6-OHDA lesion rat model.
Induction: injection of 6-OHDA into the substantia nigra or MFB
Animal Species: rats
Disease Characteristics: degeneration of dopaminergic neurons and decrease in tyrosine hydroxylas (TH) activity in the striatum
3. Transgenic PD Mouse Model
The α-synuclein A53T is the major component of LBs. Multiple α-synuclein transgenic mouse models have been generated to clarify its physiological and pathologic functions. These transgenic mice overexpress either wild-type or PD-associated mutated human α-synuclein (such as A53T, A30P) under the control of PDGF, Prnp or mThy1 promoter, to mimic pathological features of PD patients.
Animal Species: PDGF-SNCA (A53T) transgenic mice, Prnp-SNCA (A53T) transgenic mice, mThy1-SNCA transgenic mice
Disease Characteristics: α-syn inclusions distributed in multiple places, slight degradation of hydroxylase-positive fibers in the striatum
Positive Drug
L-dopamine
Clinical Assessment of PD Models
(1) Blood routine and biochemistry
(2) Open field, Pole test
(3) MRI imaging or SPECT imaging
(4) Biomarker analysis: DA and its metabolites
(5) Histopathology: H&E staining, immunohistochemistry (TH neuron)
Inquiries
Request a quote now, or email us at BD@greentech-bio.com to inquire about our services or obtain a quote for your project.
References
1. Haque ME, et al. The Neuroprotective Effects of GPR4 Inhibition through the Attenuation of Caspase Mediated Apoptotic Cell Death in an MPTP Induced Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 28;22(9):4674. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094674. PMID: 33925146; PMCID: PMC8125349.
2. Fernagut PO, Chesselet MF. Alpha-synuclein and transgenic mouse models. Neurobiol Dis. 2004 Nov;17(2):123-30. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2004.07.001. PMID: 15474350.