Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis Model
Radiation-induced oral mucositis (RIOM) represents a normal oral cavity tissue injury in cancer patients, especially in head and neck cancer patients, resulting from radiotherapy. RIOM impacts quality of life and slows the cancer therapy, remaining a huge challenge for radiation therapy. Apoptosis, cell proliferation, inflammation, and wound healing play different roles in the pathological development of RIOM.
Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis Rodent Models
Greentech Bioscience offers models for oral mucositis induced by radiation in rats or golden hamsters for preclinical pharmacological studies. Hamsters have been used widely to investigate the pathogenesis and inflammatory processes involved in oral mucositis due to the similar features of the hamster and human oral cavity, such as similar onset of oral mucositis, bacterial flora and blood cell count.
Induction: Before irradiation, animals are anesthetized and tongue of rats or the cheek pouch of golden hamsters is everted and fixed in position. Other parts of the body are protected with a lead shield. The tongue of rats or the cheek pouch of golden hamsters receive single or repeated radiation exposure at doses ranging from 25~40 Gy.
Model Characteristics: redness, edema and ulcers in the tongue/oral mucosa; inflammatory cell infiltration; epithelial cells with disintegration and necrosis; weight loss.
Animal Species
Rats, golden hamsters
Clinical Assessment
(1) Survival, food/water intake, body weight
(2) Oral mucosal injury score
(3) Histopathology: H&E, Masson, Toluidine blue staining
Case Study
Model of oral mucositis in rats
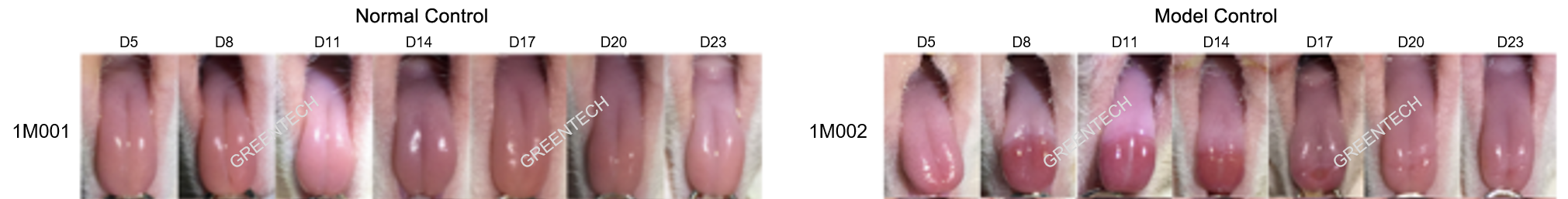
Figure 1. Macroscopic appearance of rat model for oral mucositis induced by irradiation.
Inquiries
Request a quote now, or email us at BD@greentech-bio.com to inquire about our services or obtain a quote for your project.
References
1. Yang L, Pan J. Therapeutic Effect of Ecdysterone Combine Paeonol Oral Cavity Direct Administered on Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis in Rats. Int J Mol Sci,2019,15:.
2. Kim HJ, et al. Protective Effects of N-Acetylcysteine against Radiation-Induced Oral Mucositis In Vitro and In Vivo.Cancer Res Treat,2020,4:1019-1030.